It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
Consequences of price floor and price ceiling.
Price ceilings and price floors.
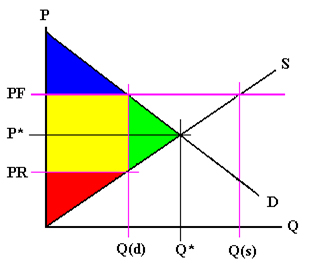
Efficiency and price floors and ceilings.
In general price ceilings contradict the free enterprise capitalist economic culture of the united states.
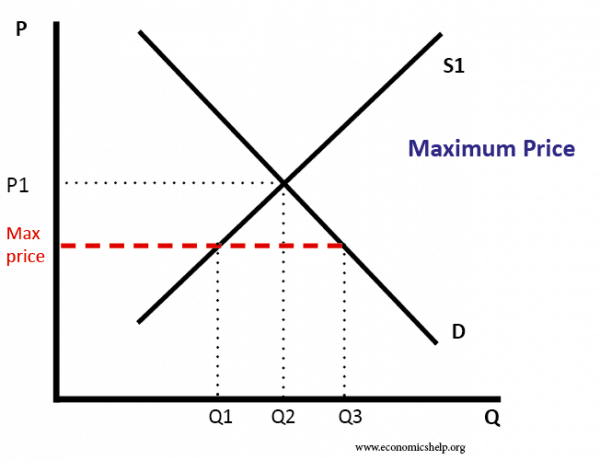
It represents an upper limit on the price of something.
This is the currently selected item.
In the end even with good intentions a price floor can hurt society more than it helps.
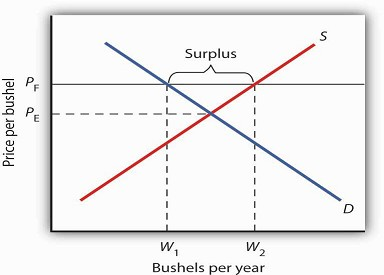
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
If wheat has a price ceiling of 400 per metric tonne 400 is the highest.
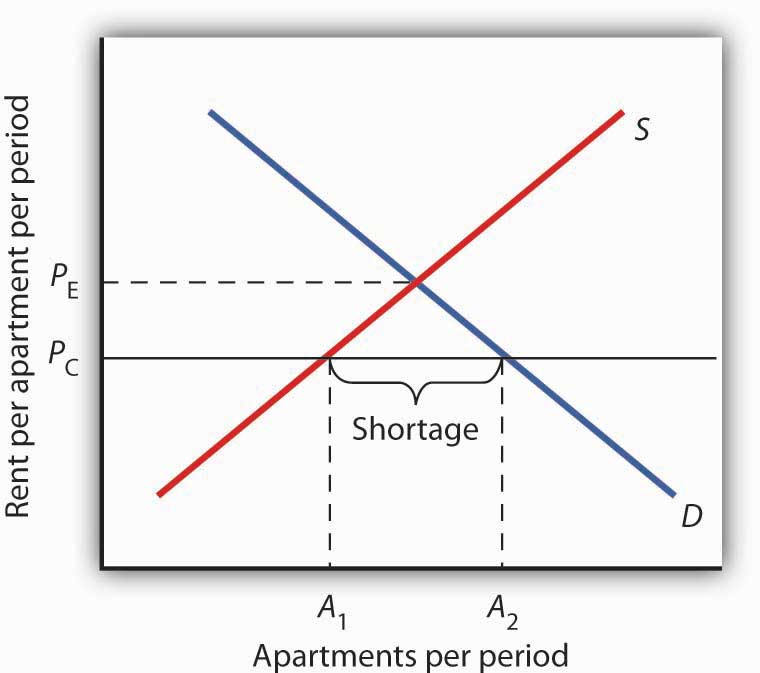
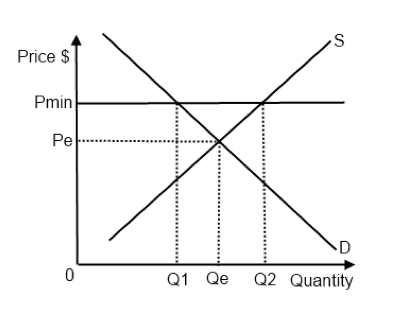
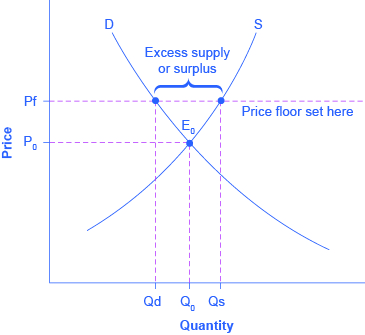
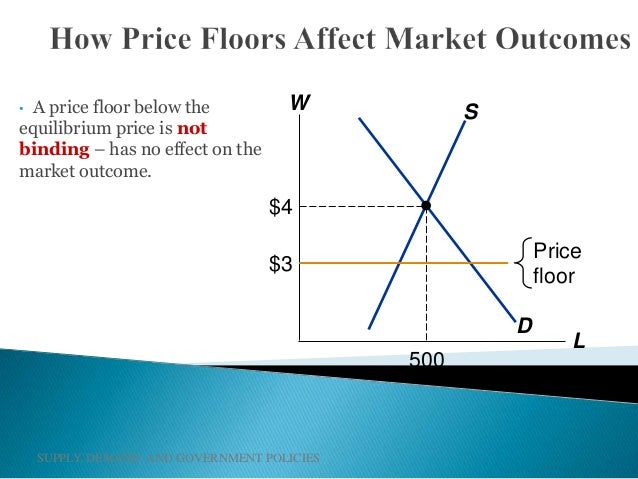
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
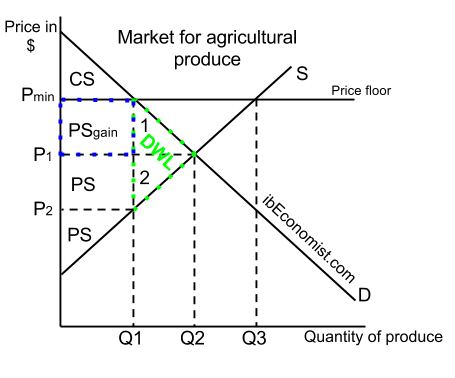
The original consumer surplus is g h j and producer surplus is i k.
In the 1970s the u s.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
Effects of a price floor.
The price floor definition in economics is the minimum price allowed for a particular good or service.
For example labor costs in the united states have a price floor of.
Real life example of a price ceiling.
It may help farmers or the few workers that get to work for minimum wage but it does not always help everyone else.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
Price and quantity controls.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
The current equilibrium is 8 per movie ticket with 1 800 people attending movies.
The price ceiling definition is the maximum price allowed for a particular good or service.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
A price ceiling prevents a price from rising above the ceiling.
The opposite of a price ceiling is a price floor which sets a minimum price at which a product or service can be sold.
When price floors are set it means that the government imposes a minimum price for a product.